How to measure collaboration in software development
A knowledge-centric approach.
Abstract
Software development is a complex process that requires the collaboration of multiple team members. But, how do you measure the efficiency of this collaboration?
Software developers apply their knowledge to deliver desired outcomes. They discover knowledge about "what" tangible output to produce and how to produce it.
Collaboration is a knowledge discovery process that acquires missing information from personal sources. It enables developers to share their knowledge and discover new information that they wouldn't have found on their own.
To measure the efficiency of collaboration, we need to measure the efficiency of knowledge discovery. The more efficient the knowledge discovery process, the more efficient the collaboration.
KEDEHub allows you to measure the knowledge discovered in software development, using the scientifically backed and patented metric - Knowledge Discovery Efficiency (KEDE). With KEDEHub, you can measure the efficiency of collaboration, productivity, and happiness of your team.
What is collaboration?
“An organization can acquire more information than any one individual, for it can have each member perform different experiments. Thus, the limitations on an individual's capacity are overcome.” ~ Arrow [2]
Collaboration involves the active engagement of multiple individuals or teams to achieve a common goal. It allows the sharing of unique perspectives, experiences, and skills, thereby facilitating a more diverse and comprehensive problem-solving approach. In software development, for example, collaboration could involve developers, testers, designers, project managers, and clients working together to deliver a successful product.
Software development is a process of going from 0% knowledge about an idea, to 100% knowledge of a finished product - ready for delivery to a customer.
Software developers are engaged in a Knowledge Discovery Process consisting of asking questions in order to acquire the missing information about "what" tangible output to produce and how to produce it. We know there was knowledge discovered when we see at least one question asked.
Missing information can be acquired from two types of sources[1]:
- Personal Sources: Those that communicate information personally including insights, experiences, and skills of team members. When people collaborate, they share and combine their knowledge, skills, and experiences, leading to a more effective problem-solving process and achievement of shared goals. In this sense, collaboration amplifies individual contributions by creating a collective intelligence that exceeds the sum of its parts.
- Impersonal Sources: These are non-human sources that communicate information to broad audiences, including books, research papers, digital databases, API documentation, StackOverflow responses, coding libraries, and online audio and video. This type of information is vital as it provides a broader, often more objective viewpoint, and can provide data and insights that may not be available within the collaborating group.
In a well-functioning collaborative environment, both personal and impersonal sources of information are considered and used to acquire knowledge, solve problems, and make informed decisions. It's important to note that when we measure the efficiency of knowledge discovery, we are considering both these categories of sources. This means we account for all channels through which new information can be gained, thereby providing a comprehensive view of the organization's level of knowledge discovery efficiency.
It is not possible for two or more people to type on the same keyboard. Thus, when two or more software developers collaborate they don't work together on the manual part of knowledge work.

When software developers collaborate they work together on the knowledge part of knowledge work.
That is very much seen in practices such as Peer Programming and Mob programming. Pair programming is a software development technique in which two programmers work together at one computer. One, the driver, writes code while the other, the observer or navigator, reviews each line of code as it is typed in. The two programmers switch roles frequently[7]. Mob programming is a software development approach where the whole team works on the same thing, at the same time, in the same space, and on the same computer. With mob programming, the collaboration is extended to everyone on the team, while still using a single computer for writing the code and adding it to the source code repository[8].
Collaboration and feedback loops are interconnected, each influencing and enhancing the other in a kind of virtuous cycle, as explained here.
The principle of bounded rationality formulated by Herbert Simon states that the capacity of the human mind for formulating and solving complex problems is very small compared with the size of the problems whose solution is required for objectively rational behavior in the real world[4]. Simon defines a ""triangle of limits'':
- the individual is limited by skills, habits, and reflexes;
- by values or conceptions of purpose which may diverge from organizational goals;
- by the extent of knowledge and information possessed[5]
An organization can alter the limits to rationality of its members by creating or changing the organizational environment in which the individual's decision making takes place. Consequently, It is only because individual human beings are limited in knowledge, foresight, skill, and time that organizations are useful instruments for the achievement of human purpose[4].
The information has to be communicated if it is to be of any use to the organization. Communication channels have to be created within the organization[2]. Communication bandwidth is one of our most obvious limits,
Work setting features such as organizational hierarchy and the location of information sources can affect the flow and availability of information. Perceived accessibility of a source is an important variable governing the decision whether to use the source. Accessibility is a function of source proximity, physical effort required, as well as the psychological cost of using the source[6].
How to measure collaboration?
Software development is a complex process that requires the collaboration of multiple team members. Measuring the efficiency of this collaboration, however, is not straightforward. It's a multifaceted task that can't be reduced to a single metric.
There are tools available that, from 'inside the black box', measure the efficiency of practices— such as Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD), Pair Programming, and Code Reviews— that are designed to facilitate and enhance collaboration and shorten feedback loops in software development. However, it's also crucial to remember that it's both possible and valuable to gauge the effectiveness of collaboration from outside this 'black box'.
One way to do this is by examining the efficiency of knowledge discovery in relation to the number of active contributing software developers.
Collaboration, impersonal sources of information, and prior knowledge are integral to the process of knowledge creation, decision-making, learning, and innovation. They each bring unique benefits and, when combined, can enhance the overall effectiveness of an organization. Of those only collaboration can be affected by the number of people who work together.
- Prior knowledge doesn't depend on the number of people in the organization.
- Impersonal sources of information don't depend on the number of people in the organization. If people with access to better impersonal sources of information join, their personal capability will affect the organization only if there is collaboration in place.
- Collaboration depends on the number of people in an organization. Collaboration can be negatively affected by the coordination overhead. Teams of non-collaborating developers become less productive ,as they grow in size.
Thus, we can conclude that if we consider the efficiency of a knowledge discovery relative to the number of contributing software developers then we can infer if the collaboration is increasing or decreasing.
The number of contributing developers can be determined by counting those actively participating in a project over a certain period of time.
The efficiency of knowledge discovery, on the other hand, can be understood in terms of how rapidly and effectively missing information is acquired and integrated into the team's work. This can be reflected in the time taken to incorporate missing information, the completeness or accuracy of the understanding of new information, and the impact of the new information on the team's productivity or the quality of their output.
Knowledge Discovery Efficiency (KEDE) is a metric that can be used to measure the efficiency of knowledge discovery in software development. We will refer to an organization's efficiency of knowledge discovery as its 'capability.'
Consider the time-series diagram below, which illustrates the interplay between an organization's size and its capability over time.
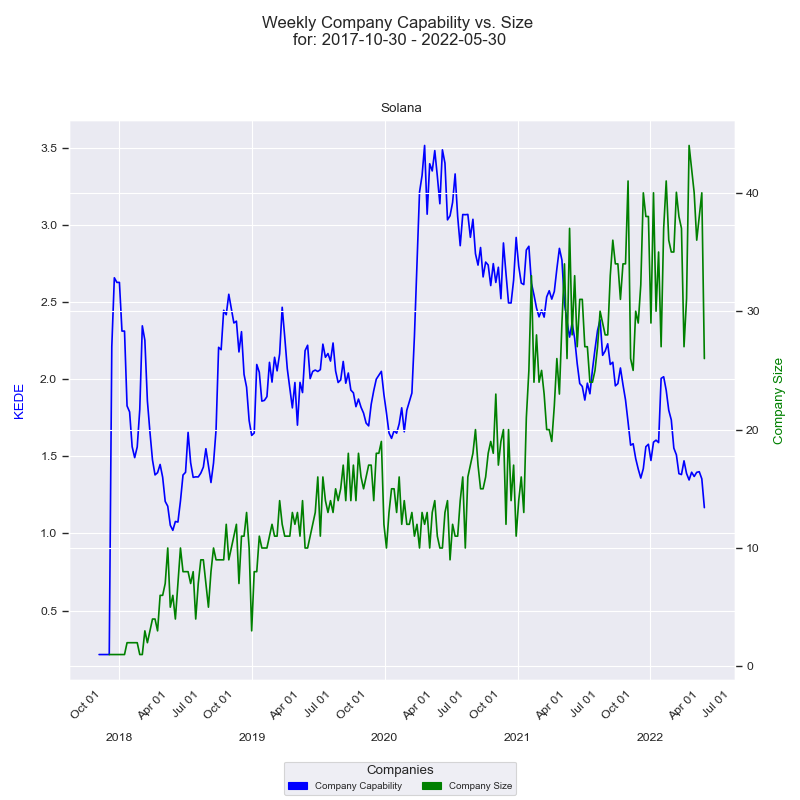
The x-axis represents the quarters, while the y-axis on the left displays the 'capability' in terms of Weekly KEDE values. The dark blue line in the diagram represents the average Weekly KEDE for all developers who contributed to the company's projects in a given week, calculated using Exponential Weighted Moving Average (EWMA). This line offers a visual representation of how the organization's capability fluctuates over time.
The right y-axis showcases the size of the company, depicted by the number of developers who contributed to the company's projects in a given week. The green line represents the company's size over time, with each point marking the count of contributing developers for that week. A detailed construction of the diagram can be found here.
The diagram displays a notable period where there is an inverse correlation between the company's size and its capability. Over the span of more than two years, the company size surged from 20 to 44, a substantial 120% increase. Conversely, during the same period, the capability steadily declined from 3.6 to 1.3, indicating a 64% decrease. The diagram illustrates a trend wherein the efficiency of knowledge discovery decreases as the number of contributing software developers increases.
Another way to visualize the relationship between the efficiency of knowledge discovery and the number of developers is through a histogram. This chart shows the frequency distribution of the company's 'capability' against the number of contributing developers over time.
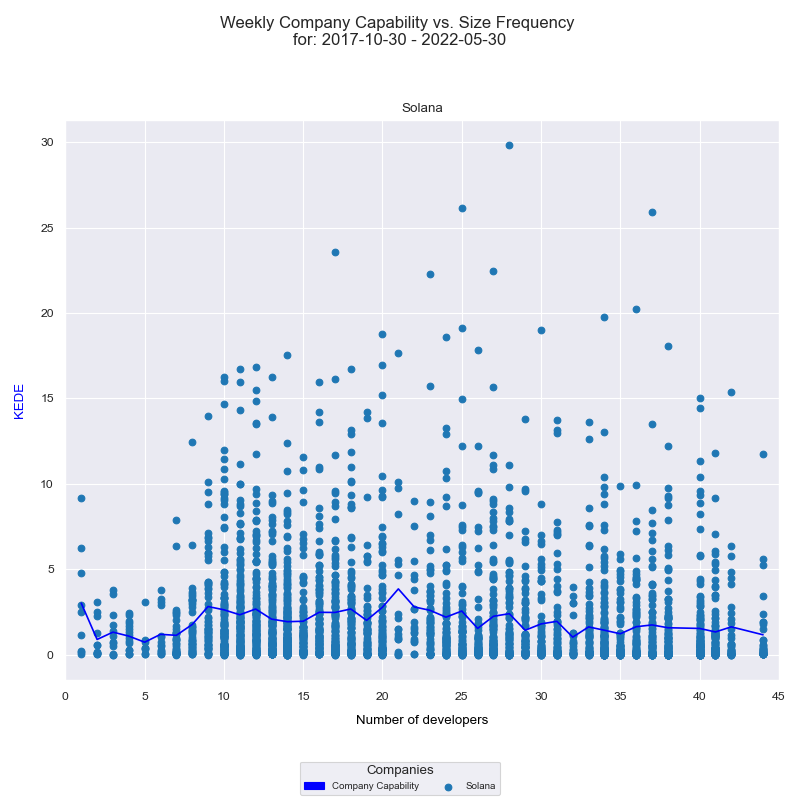
The x-axis displays the number of developers who contributed to any of the projects in a given week, while the y-axis represents the weekly KEDE values. Each individual developer's aggregated Weekly capability is presented as a light blue dot on the diagram, while the dark blue line represents the average weekly capability for all developers calculated by arithmetic mean. A detailed explanation of how this diagram was constructed can be found here. Analyzing this histogram, we once again observe that the efficiency of knowledge discovery tends to decrease as the number of contributing software developers increases.
Interpreting these two diagrams together, we might suggest potential issues with the level of collaboration in the organization. Challenges could arise in terms of communication, coordination, knowledge silos, individual contribution, or even information overload. While more contributors are generally beneficial, managing the complexity requires effective strategies, clear communication, and robust systems. However, it's crucial to remember that we are observing these trends from 'outside the black box'. The actual cause could be a combination of these factors, or even something entirely different. A more accurate understanding would require 'looking inside the box' to ascertain the underlying reasons.
KEDEHub allows you to make comparisons among your company's functional areas and between your company and others. You are now able to unleash your company's untapped collaboration potential by objectively and scientifically answer questions such as:
- What is the level of a company's collaboration compared with the average level in the industry?
- Did the latest increase in headcount increase a company's collaboration?
- Did the Agile transformation increase a company's collaboration?
- Did the latest re-org increase a company's collaboration?
- What is the level of a team's collaboration?
- Did the new recruits increase a team's collaboration?
- What is the level of a team's collaboration compared with all other teams working on the same project?
Works Cited
1. Choo, C. (1994). Perception and use of information sources by chief executives in environmental scanning, Library & Information Science Research, Volume 16, Issue 1
2. Arrow, K. (1974) The Limits of Organization.New York: Norton
3. Simon, H. (1947) Administrative Behavior: A Study of Decision-Making Processes in Administrative Organization. New York: Macmillan.
4. Simon, H. A. (1957). Models of man - social and rational. New York: John Wiley.
5. Simon, H. A. (1976). Administrative behavior. (3rd edition) New York: Free Press.
6. Choo, C. (2005). The Knowing Organization: How Organizations Use Information to Construct Meaning, Create Knowledge, and Make Decisions. : Oxford University Press.
7. L. Williams, "Integrating pair programming into a software development process," Proceedings 14th Conference on Software Engineering Education and Training. 'In search of a software engineering profession' (Cat. No.PR01059), 2001, pp. 27-36, doi: 10.1109/CSEE.2001.913816.
8. Zuill, Woody (2014). "Mob Programming: A Whole Team Approach". Agile2014 Conference Experience Reports:
How to cite:
Bakardzhiev D.V. (2022) How to measure collaboration in software development? https://docs.kedehub.io/kede/kede-collaboration.html
Getting started


