Introduction
In the dynamic world of software development, the quest for efficiency and effectiveness is relentless. Among the various methodologies that have emerged, Scrum stands out as a beacon of agility and adaptability. Originating from the early 1990s, Scrum has revolutionized the way teams approach complex software development projects. At its core, Scrum is an agile framework designed to foster team collaboration, promote iterative progress, and facilitate the rapid adaptation to changing requirements. This methodology breaks down large projects into manageable sprints, with each sprint delivering a potentially shippable product increment.
The knowledge-centric perspective on Scrum was first presented in 2001 in the book “Agile Software Development with Scrum” by Ken Schwaber and Mike Beedle[5]. In their book, there is a pivotal section titled “Knowledge Creation View of Scrum.” It posits that software development involves creating new products, which inherently requires research and creativity. The common thread between research and creativity is knowledge creation. Gathering requirements for an application indicates they initially exist in a tacit form. As design decisions are made, this tacit knowledge is transformed into explicit knowledge, eventually captured in the code or an executable model. From this perspective, software is essentially codified and explicit knowledge.
The purpose of this article is to delve deeper into the Scrum framework from that unique perspective - one that aligns knowledge and learning with the Scrum processes. We aim to explore Scrum through a knowledge-centric lens, integrating the concept of Flow, as articulated by Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi Flow, the state of being completely immersed and focused on the task at hand, is crucial for maximizing productivity and satisfaction in work environments. By examining how Scrum practices can facilitate the achievement of Flow, we can uncover new insights into enhancing team performance and project outcomes.
Moreover, this article seeks to introduce the concept of KEDE within the context of Scrum. KEDE provides a quantifiable measure of the balance between a team member's existing knowledge and the new challenges encountered during a project. This metric offers a novel way to gauge learning and development progress within the Scrum framework, thereby adding a new dimension to understanding and improving software development processes.
By integrating these concepts into Scrum practices, we hope to offer a fresh perspective that not only enhances the understanding of Scrum but also provides practical insights for implementing Scrum more effectively in software development projects.
Defining Scrum and Its Key Principles
Scrum is a widely-used Agile framework that assists teams in managing and delivering complex projects effectively. Scrum teams are self-organizing, comprising three central roles: the Scrum Master, who facilitates and removes obstacles; the Product Owner, who represents the customer's interests and priorities; and the Development Team, responsible for creating the product[1].
Scrum's foundation is built on three pillars: transparency, inspection, and adaptation. Transparency involves making all aspects of the work visible to all members of the Scrum Team. Inspection includes regular checks on the product and the process to detect undesirable deviations outside acceptable limits, while adaptation allows for regular adjustment and alignment based on feedback to prevent further deviations[1].
The key principles that underpin Scrum include:
- Iterative Development: At its core, Scrum is an iterative and incremental process, with projects divided into sprints, which are short, time-boxed periods (usually two to four weeks). The Sprint Goal is the single objective for the Sprint. The Sprint Goal is created during the Sprint Planning event and then added to the Sprint Backlog. Each sprint results in a potentially shippable product increment. Work cannot be considered part of an Increment unless it meets the Definition of Done. The Definition of Done is a formal description of the state of the Increment when it meets the quality measures required for the product.
- Collaboration: It leverages the collective knowledge and skills of the team to tackle complex problems effectively. It emphasizes teamwork, collective accountability, and continuous interaction with stakeholders to ensure that the end product aligns with customer needs and expectations.
- Feedback: Feedback plays an integral role in the Scrum framework, serving as a critical tool for continuous improvement and effective problem-solving. It not only influences product adjustments but also helps in refining team processes. The importance of feedback underpins Scrum's iterative nature, promoting growth, learning, and adaptation at every step. Through regular meetings like Sprint Reviews and Retrospectives, Scrum promotes introspection and the continuous enhancement of processes, tools, and team dynamics.
Scrum enables teams to focus on delivering value in the shortest possible time, encourages continuous feedback, and empowers team members to take ownership of their work. Scrum provides a structure that helps teams navigate the complexities and uncertainties inherent in software development.
The Knowledge-centric perspective on Scrum
In software development, gathering requirements is often the first step in transforming ideas into reality. Initially, these requirements exist in a tacit form—knowledge that's understood intuitively but not yet articulated. As design decisions are made, this tacit knowledge is transformed into explicit knowledge, eventually captured in the code or an executable model. From this perspective, software is essentially codified and explicit knowledge.
Explicit knowledge refers to information that can be transmitted in a systematic language, such as code, documents, models, and graphics in software development. This is in contrast to tacit knowledge, which is based on experience and typically reflected in intuitions and reactions but not externalized. In software development, tacit knowledge often resides with individuals who have specialized skills and experience, such as software users, domain experts, and seasoned programmers.
From the perspective of knowledge creation, Scrum facilitates the generation of knowledge through cycles of socialization, externalization, combination, and internalization of knowledge, as described by Takeuchi and Nonaka[6]. These cycles are illustrated in the knowledge conversion model:
- Socialization: Direct conveyance of tacit knowledge through shared experiences.
- Externalization: Articulating tacit knowledge into explicit concepts.
- Combination: Systematizing concepts into a coherent knowledge system.
- Internalization: Embodying explicit knowledge into tacit, operational knowledge.
Daily Scrum meetings exemplify this cycle. A team member’s tacit knowledge is shared (socialized) during the meeting. This knowledge is then externalized, often resulting in items added to the Sprint Backlog or simply shared as useful information for other team members. Other team members can combine this newly externalized knowledge with their own, and internalize it to use throughout their workday. The continuous application of this cycle through Scrum practices creates a Knowledge Spiral, rapidly spreading knowledge throughout the organization.
A Scrum team creates knowledge through these mechanisms:
- Sharing tacit knowledge: For example, developers exchange ideas about requirements or design in a Scrum meeting or while working collaboratively.
- Creating concepts: Such as developing design models like packages, classes, relationships, and interactions.
- Justifying concepts: Developers validate requirements and designs.
- Building an archetype: For example, creating a prototype.
- Cross-leveling of knowledge: This process restarts the cycle, facilitating continuous knowledge creation.
Though these mechanisms are listed sequentially, Scrum encourages adaptive movement between them, allowing developers to navigate the knowledge creation process fluidly.
Burndown Chart for Knowledge Work
Traditionally, a Burndown chart shows the amount of work remaining over time, helping teams visualize progress and predict task completion. However, when viewed through a knowledge-centric lens, we can redefine this tool to track the number of unanswered questions—representing the gap between required and prior knowledge— over the duration of a sprint.
Components:
- X-Axis: Represents time, usually in days within a sprint.
- Y-Axis: Represents the number of unanswered questions.
- Ideal Work Remaining Line: A straight line from the total number of unanswered questions at the start of the sprint to zero at the end of the sprint. This represents the ideal progress where questions are answered at a consistent rate.
- Actual Work Remaining Line: A line that shows the actual number of unanswered questions at the end of each day.
Creating and Using the Burndown Chart:
- Identify Total Unanswered Questions: Determine the total number of unanswered questions (knowledge gaps) at the beginning of the sprint.
- Plot Ideal Line: Draw a line from the total unanswered questions on day 1 to zero unanswered questions on the last day of the sprint.
- Update Daily: At the end of each day, calculate the remaining unanswered questions and plot this on the chart.
- Analyze: Compare the actual work remaining line with the ideal work remaining line to assess progress in closing knowledge gaps. If the actual line is above the ideal line, the team is behind schedule in answering questions. If it's below, they are ahead.
Example of a Burndown Chart for Unanswered Questions
Imagine a sprint that lasts 10 days with a total of 50 unanswered questions to address. The Burndown chart would look like this:
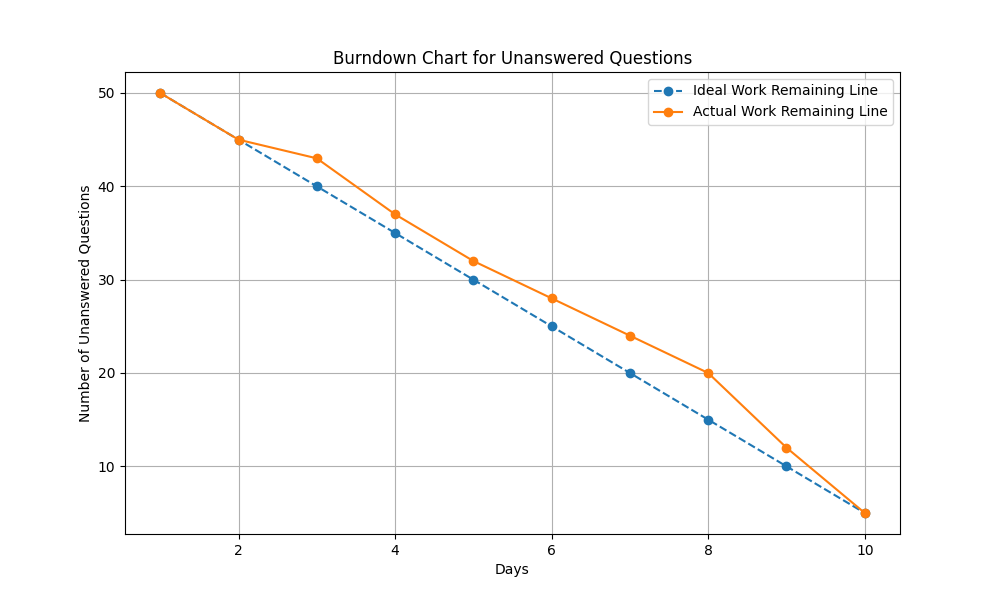
- X-Axis: Days (1 to 10)
- Y-Axis: Number of Unanswered Questions (0 to 50)
- Ideal Work Remaining Line: A diagonal line from 50 unanswered questions on day 1 to 0 unanswered questions on day 10.
- Actual Work Remaining Line: This line is updated daily to reflect the actual number of unanswered questions at the end of each day.
Benefits:
- Visibility: Provides a clear visual of progress in addressing knowledge gaps.
- Predictability: Helps in predicting if the team can close all knowledge gaps by the end of the sprint.
- Motivation: Can motivate the team by visually showing their progress in answering questions.
- Transparency: Enhances transparency within the team and with stakeholders about the progress in addressing knowledge gaps.
By quantifying knowledge gaps as unanswered questions and tracking them using a Burndown chart, teams can effectively monitor and manage their progress in addressing the cognitive aspects of their tasks, ensuring they are on track to meet their sprint goal.
Understanding Scrum and the Flow State
Introducing the Concept of Flow
The concept of Flow, as coined by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, refers to a state of heightened focus and immersion in activities. People in a state of Flow lose their sense of time, feel in control of the task at hand, and experience an intrinsic sense of enjoyment and fulfillment[2].
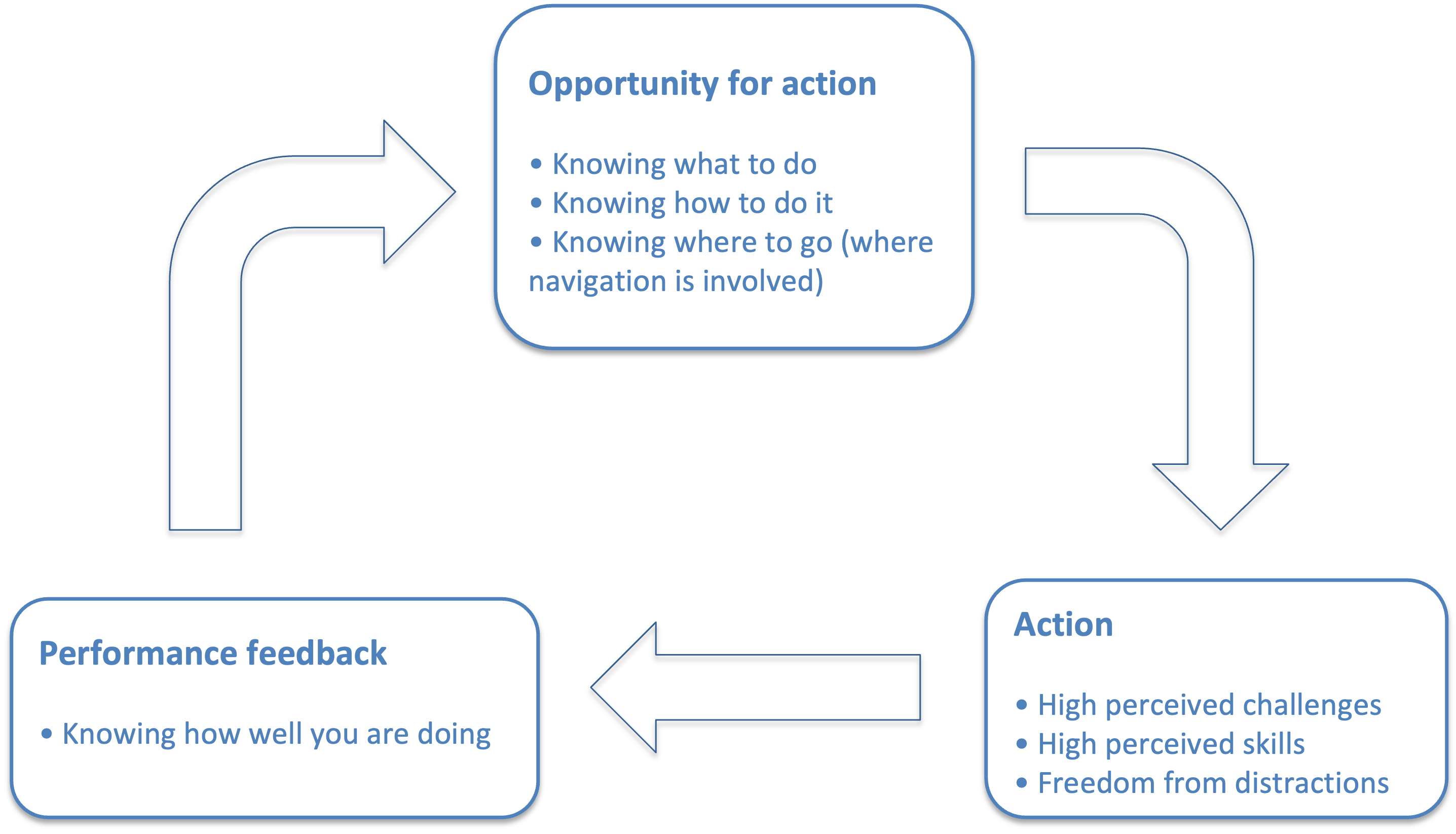
To enter and maintain a flow state, the following conditions should be met[3]:
- The opportunity for action, with a clear and attainable goal. That doesn't mean having an overall goal for the activity, but knowing what to do next from moment to moment[9]
- An action with a balance between skill level and challenge, meaning that the activity is neither too easy nor too difficult.
- Clear and immediate feedback, so that successes and failures are apparent and behavior can be adjusted as needed.
The balance should be established for each task the developer will face. Once the conditions for action are in place, the developer is able to engage in a series of challenging tasks that are neither too difficult (not overwhelming) nor too easy (not boring). By balancing each task, we can create the conditions for entering flow for each set of tasks, each feature, and ultimately, for the scope of the project.
When the conditions for flow are met, they create a feedback loop between action and feedback that allows for continuous, effortless tuning of performance while taking action. This feedback loop makes an activity worth doing for its own sake[3].
Introducing the Knowledge-centric perspective
The knowledge-centric perspective on software development, treats knowledge as the fuel that drives the software development engine. Central to this perspective is understanding the knowledge gap between what a developer knows and what they need to know to effectively complete tasks. Bridging this gap involves discovering and applying new knowledge.
When individual capability significantly exceeds task complexity, the knowledge gap becomes too narrow, leading to wasted potential and boredom. On the other hand, if task complexity surpasses individual capability, the knowledge gap widens, leading to stress and low productivity. A well-balanced gap keeps developers in the Flow state, fully immersed and focused on their work, leading to higher productivity and job satisfaction.
To ascertain whether developers achieve a state of Flow, it's essential to assess the presence of three key conditions: a clear and attainable goal, a balance between skill level and challenge, and clear and immediate feedback. Assessing these conditions in real-time, as a developer works on a task, is impractical due to the inaccessibility of the developer's cognitive process.
However, a post-task completion analysis offers a viable alternative, as all three Flow conditions are intricately linked to knowledge. Specifically:
- Goals: Understanding the task involves knowing what to do, how to do it, and the next steps to take.
- Skill and Challenge Balance: This is about the knowledge a developer possesses versus what they need to know to complete tasks effectively.
- Feedback: This pertains to recognizing the correctness of actions and making necessary adjustments.
This knowledge is categorized into two types: 'prior knowledge' (what the developer already knows) and 'required knowledge' (what the developer needs to know for the task). The 'knowledge gap' is the difference between these two, measured in bits. Therefore, measuring the knowledge acquired post-task can indicate whether the developer was in a state of Flow. We quantify this knowledge gap in bits of information, allowing us to measure the knowledge to be discovered. This approach facilitates meaningful comparisons across different contexts, programming languages, and applications.
Relevance of Flow to Scrum
Jeff Sutherland, one of the co-creators of Scrum, has made a significant claim: Scrum is a pathway to achieving a state of 'Flow,' leading teams to a level of true mastery[4]. Indeed, when viewed through a knowledge-centric lens, Scrum is in a striking alignment with the concept of Flow. This alignment is rooted in the core practices and artifacts of Scrum, each contributing to creating an environment where Flow can be achieved and sustained.
- Goal Clarity: The Sprint Goal in Scrum is a clear, concise objective set for each Sprint, providing a focal point for the team's efforts The Sprint Backlog is composed of the Sprint Goal (why), the set of Product Backlog items selected for the Sprint (what), as well as an actionable plan for delivering the Increment (how)[1]. This clarity and visibility align with the Flow requirement of having a clear and proximal goal. The Daily Scrum, a key event in the Scrum framework, further supports this by inspecting the progress toward the Sprint Goal and planning the next steps.
- Balanced Challenges and Skills: The self-organizing nature of Scrum teams allows for flexibility and adaptability in task allocation, ensuring that each member can work on tasks that align with their skills while still offering opportunities for growth and learning. This balance is crucial for Flow, as it ensures that team members are engaged in work that is neither too easy to be boring nor too difficult to be overwhelming.
- Feedback and Adaptation: The regular feedback loops in Scrum, ceremonies like Daily Stand-ups and Sprint Reviews, Scrum provides immediate insights into work progress and challenges faced by the team. This constant feedback loop allows for immediate adjustments and realignment of efforts, ensuring that any obstacles to achieving the Sprint Goal can be quickly identified and addressed. This feedback is crucial for maintaining the Flow state, by providing the necessary information to adjust actions and maintain focus on the goal.
In essence, Scrum's structured yet flexible approach, characterized by clear goal, a balance between challenges and skills, and continuous feedback, creates an optimal environment for team members to achieve a state of Flow. From this knowledge-centric perspective, Scrum is more than a framework for managing projects; it is a pathway to achieving peak performance and deep engagement in work.
Operational Guide
Scrum's iterative nature ensures that work is broken down into manageable components, reducing overwhelm and increasing the likelihood of experiencing Flow. Each sprint provides a focused timeframe to concentrate on specific tasks, enhancing the team's ability to immerse themselves deeply in their work.
Furthermore, the collaborative aspect of Scrum = with team members working closely, sharing responsibilities, and communicating regularly - creates a supportive environment that is conducive to Flow. The synergy of a well-functioning Scrum team can elevate the individual experiences of Flow, leading to collective efficiency and satisfaction.
Understanding the synergies between Scrum and the Flow state reveals how Scrum's practices and principles are not just about managing work efficiently, but also about creating an optimal work environment that enhances both the individual and collective experiences of team members.
Balancing Skills and Challenges in Scrum
Sprint Planning and Backlogs: Ensuring a Balance
One of the key ways in which Scrum ensures a balance between an individual's skills and the challenges of tasks is through Sprint Planning and the management of Backlogs.
- Sprint Planning: This is a fundamental ceremony in Scrum where the team collectively decides what to work on in the upcoming sprint. During this planning phase, tasks are chosen from the Product Backlog and moved into the Sprint Backlog. It's here that the balance is delicately negotiated - tasks are selected not only based on priority but also on how clear they are - considering the team's capacity and individual skills. This process ensures that the tasks are challenging enough to be engaging but not so difficult that they become overwhelming.
- Product and Sprint Backlogs: The Product Backlog is a dynamic list of features, changes, fixes, and enhancements that serves as the input for Sprint Planning. The Sprint Backlog, on the other hand, is a subset of the Product Backlog, tailored for a specific sprint. These backlogs are crucial for maintaining the balance between skills and challenges as they are constantly refined and reprioritized. This ensures that the work remains aligned with team capabilities and project goal.
Matching Team Capabilities with Project Complexity
The effectiveness of Scrum largely depends on how well the team's capabilities are matched with the complexity of the project. This matching process is vital for several reasons:
- Optimal Performance: When tasks align well with a team member's abilities, it leads to higher productivity and quality of work. Scrum facilitates this by allowing teams to self-organize and select tasks that align with their skills and interests.
- Enhanced Learning and Growth: Scrum encourages continuous learning. When team members take on tasks that slightly exceed their current abilities, it promotes skill development. This calculated stretch is essential for personal growth and team evolution.
- Preventing Burnout and Disengagement: If the challenge is too great, team members can become overwhelmed and stressed, leading to burnout. Conversely, if the work is too easy, it can lead to boredom and disengagement. Scrum aims to strike the right balance, keeping team members engaged and motivated.
- Adaptive Planning: Scrum's iterative approach allows for frequent reassessment of the balance between skills and challenges. During Sprint Retrospectives, teams reflect on what went well and what could be improved, providing opportunities to adjust task assignments and processes to better match team capabilities.
In conclusion, balancing skills and challenges is a dynamic and ongoing process in Scrum. Through effective Sprint Planning, management of Backlogs, and a keen understanding of team capabilities, Scrum enables teams to not only meet project demands efficiently but also fosters an environment of continuous learning and growth, leading to sustained high performance.
The Role of Clear and Attainable Goals
Clarity and Direction through Scrum Artifacts
Scrum framework is built around various artifacts that provide clear and attainable goals, which are fundamental for achieving a state of Flow. These artifacts, primarily the Product Backlog and Sprint Goals, play a pivotal role in setting clear directions for the team.
- Product Backlog: This is a comprehensive list of features, enhancements, and fixes that the product needs. The Product Owner manages this backlog, ensuring it reflects customer needs and aligns with the project's long-term vision. The Product Backlog serves as a roadmap, offering a clear view of what needs to be achieved and allowing the team to understand the bigger picture.
- Sprint Goal: The Sprint Goal is a singular, concise statement of what the team plans to achieve during the Sprint. This goal is formulated during the Sprint Planning session and provides a clear focus for the team's efforts over the Sprint's duration. The Sprint Goal is essential as it offers a specific target to aim for, ensuring that all the work in the Sprint contributes to a cohesive outcome.
Breaking Down Complex Projects into Manageable Tasks within Sprints
Scrum excels in transforming complex project objectives into manageable and actionable tasks within each Sprint, a process that is central to maintaining a state of Flow for the team.
- Sprint Planning: During this session, the team selects items from the Product Backlog to include in the Sprint, with the Sprint Goal in mind. This phase involves breaking down larger items into smaller, more manageable tasks. The process ensures that each task is attainable and directly contributes to the Sprint Goal, fostering a sense of progress and achievement.
- Task Allocation and Estimation: Team members collaboratively decide who will work on each task, taking into account individual skills and interests. This phase also involves estimating the effort required for each task, contributing to realistic expectations and achievable goal for the Sprint.
- Daily Scrum Meetings: These brief, daily sessions provide a platform for the team to synchronize activities and discuss challenges. The constant focus on the Sprint Goal during these meetings ensures that the team remains aligned and motivated, reinforcing the commitment to the singular objective of the Sprint.
Scrum’s emphasis on clear and attainable goals, particularly through the singular Sprint Goal and the well-defined Product Backlog, is instrumental in guiding the team's efforts and maintaining a productive state of Flow. By breaking down complex projects into manageable tasks aligned with the Sprint Goal, Scrum ensures that teams can focus effectively and contribute meaningfully to the project's success.
Feedback Loops and Continuous Improvement
The Significance of Regular Scrum Ceremonies
In Scrum, regular ceremonies such as Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Reviews, and Sprint Retrospectives are crucial for creating effective feedback loops and fostering an environment of continuous improvement.
- Daily Stand-ups: These brief daily meetings are a platform for team members to update each other on their progress, challenges, and plans for the day. This practice ensures that feedback is immediate and relevant, allowing team members to quickly adjust their actions and stay aligned with the Sprint Goal.
- Sprint Reviews: At the end of each Sprint, the team presents the work accomplished to stakeholders during the Sprint Review. This ceremony provides valuable feedback on the product increment from both the internal team and external stakeholders. It's an opportunity to gauge the success of the Sprint and gather insights for future work.
- Sprint Retrospectives: Perhaps the most critical for continuous improvement, Retrospectives are sessions where the team reflects on the past Sprint. They discuss what went well, what didn’t, and how processes can be improved. This ceremony fosters a culture of introspection and collective growth, allowing teams to evolve their practices and become more effective over time.
Connecting Feedback Loops with the Flow State
The requirement for clear and immediate feedback in achieving a state of Flow is deeply integrated into these Scrum ceremonies.
- Immediate Feedback for Behavioral Adjustment: In the context of Flow, immediate feedback allows individuals to adjust their behavior and performance on the spot. Daily Stand-ups and Sprint Reviews serve this purpose by providing regular checkpoints for feedback and adjustment.
- Clarity in Goals and Progress: The clarity provided by regular feedback helps maintain the focus necessary for Flow. Knowing where one stands in relation to the Sprint Goal and receiving immediate feedback on progress are key to sustaining this focused state.
- Enhanced Sense of Control and Achievement: The feedback from these Scrum ceremonies contributes to a sense of control and achievement among team members. When individuals see the results of their efforts and understand how their work contributes to the larger goal, it enhances their engagement and motivation, key elements of the Flow state.
- Cultivating a Learning Environment: Continuous feedback and improvement foster a learning environment conducive to Flow. The adaptability and growth encouraged by Sprint Retrospectives ensure that the team is constantly enhancing their skills and approaches, keeping the challenges fresh and engaging.
In summary, the feedback loops created through Scrum's regular ceremonies are fundamental in providing the immediate and clear feedback necessary for achieving and maintaining the state of Flow. They allow for quick adjustments, ensure clarity of goals and progress, and foster a continuous learning environment that keeps team members engaged, satisfied, and productive.
Checklists
The checklists provide for an efficient and effective Scrum from a knowledge-centric perspective with focus on ensuring alignment, knowledge flow, and team productivity. Each checklist is designed to guide teams through critical elements such as shared understanding, challenge-skill balance, prioritization, feedback loops, clarification of unknowns, realistic commitments, and contingency plans. By auditing these areas, teams can ensure that planning sessions lead to successful sprints, promoting flow and maximizing value delivery while maintaining adaptability and learning opportunities throughout the sprint.
Sprint Planning Checklist
A sprint planning meeting is conducted before the start of a sprint. The purpose of this meeting is to determine the sprint plan and set a sprint goal.
Here’s a checklist for efficient and effective Sprint Planning from a knowledge-centric perspective:
-
Shared Understanding:
Objective: Ensure all team members understand the sprint goal and the backlog items. Transform tacit knowledge into explicit tasks.
-
Was the sprint goal clearly defined?
- Was the sprint goal agreed upon and understood by the entire team?
- Were questions raised by team members adequately addressed?
-
Were backlog items fully explained and understood so that the team can proceed confidently into the sprint?
-
Did the product owner explain the business value of each backlog item?
Confirm whether the product owner clearly articulated why each item is important and how it contributes to the overall product vision.
- Were Definitions of Ready provided? Having a Definition of Ready means that stories must be clear, concise, and most importantly, immediately actionable.
-
Were acceptance criteria provided?
Check if the acceptance criteria were clearly defined for each item, so the team knows when a backlog item is considered "done."
-
Was technical context provided for complex items?
For more technical items, assess if the product owner or team provided necessary technical explanations, reducing confusion for development.
-
Were all team members given a chance to ask questions?
Verify if the product owner encouraged questions from the team to clarify any ambiguities in the backlog items.
-
Did the team resolve all identified ambiguities?
Check if all uncertainties about scope, requirements, or dependencies were addressed during the session.Note: Not knowing something is different from being vague. Don’t ignore the unknowns, they are the reality of doing difficult work. But don’t hide them by using vague words. Be clear when you don’t know something and frame the work in terms of gaining an understanding.
-
Was there consensus on each item’s priority and feasibility?
Evaluate if the team reached a shared understanding of each item's priority and whether it can be realistically completed within the sprint.
-
Did the product owner explain the business value of each backlog item?
-
Was the sprint plan prepared?
-
Did the development team outline a "just enough" plan for the sprint?
Was there a balance between planning enough to start, without over-planning or rigidly accounting for every minute of the sprint?
-
Was the plan a result of negotiation between the team and the product owner?
Did the team and the product owner work together to prioritize value and balance the effort required?
-
Does the plan focus on valuable outcomes?
Are team members focused on delivering outcomes aligned with the sprint goal, rather than just completing tasks?
-
Are there clear guardrails for self-organization?
Does the plan allow the team enough flexibility to self-organize and make adjustments if needed during the sprint?
-
Is there contingency in place if the sprint goal is achieved early?
Is the product backlog ordered so that the team can pick up additional work if they deliver the sprint goal ahead of schedule?
-
Did the development team outline a "just enough" plan for the sprint?
This checklist focuses on ensuring that all team members have a shared mental model of the sprint, helping to reduce misunderstandings or inefficiencies later on.
-
Was the sprint goal clearly defined?
-
Knowledge Flow:
Objective: Facilitate open discussions to surface hidden insights or dependencies.
-
Was tacit knowledge effectively transformed into explicit tasks?
- Did team members share insights based on their experiences or expertise?
- Were these insights documented in actionable tasks?
-
Were all team members encouraged to share insights and concerns?
- Did everyone have an opportunity to contribute their knowledge during the planning session?
- Were any hidden insights or relevant experiences brought up that could influence the sprint?
-
Were dependencies, risks, and challenges surfaced and discussed?
- Did team members raise potential blockers, knowledge gaps, or risks?
- Were those challenges incorporated into the sprint plan?
-
Was there a clear plan for managing knowledge gaps?
- Were there action steps to address uncertainties, such as research spikes or additional discussions with stakeholders?
- Was a process identified to handle new information that might arise during the sprint?
This section focuses on the free exchange of knowledge during Sprint Planning, ensuring that team members share what they know to improve transparency and address potential challenges.
-
Was tacit knowledge effectively transformed into explicit tasks?
-
Challenge-Skill Balance:
Objective: Match user stories and tasks to team members’ capabilities, knowledge and skills, promoting flow and motivation.
-
Were individual team members’ skills and expertise assessed?
- Did the team review each member’s strengths and areas of expertise during planning?
- Were skill inventories or matrices used to identify capabilities?
-
Were knowledge gaps identified and addressed?
- Did the team discuss any skills needed that are currently lacking?
- Are training or research tasks included in the sprint to fill these gaps?
-
Are tasks challenging enough to engage team members without overwhelming them?
- Evaluate if the tasks push the team’s skills in a way that promotes learning and growth while maintaining motivation.
- Confirm if the tasks are sufficiently motivating, helping team members feel engaged and in control of their progress.
-
Was there discussion of skill development or knowledge gaps?
- Did the team identify opportunities for team members to work on new skills or fill gaps in their expertise?
- Are team members encouraged to take on new challenges to expand their skills?
- Were pair programming or mentoring arrangements made for knowledge transfer?
-
Were communication channels established for ongoing support?
- Are regular check-ins planned to discuss progress and obstacles?
- Is there an open environment for asking questions and sharing insights?
-
Is there a plan to monitor the challenge-skill balance during the sprint?
- Will the team assess if tasks remain appropriately challenging?
- Are adjustments planned if a team member becomes overburdened or underutilized?
-
Are feedback loops established to learn from the sprint?
- Will there be a retrospective focus on how well tasks matched skills?
- Is there a process to integrate learnings into future sprint planning?
This checklist ensures that work is aligned with team member strengths while promoting a productive flow state by balancing challenge and skill.
-
Were individual team members’ skills and expertise assessed?
-
Prioritization:
Objective: Ensure backlog items are prioritized based on their value, the team's expertise, and alignment with the sprint goal.
-
Alignment with Sprint Goal
-
Are backlog items clearly linked to the sprint goal?
- Did the team ensure that the highest priority backlog items directly contribute to achieving the sprint goal?
- Were lower-priority items deprioritized or moved to future sprints?
-
Was the backlog ordered based on delivering value early?
- Did the product owner prioritize items that will bring the most immediate business or customer value?
-
Are backlog items clearly linked to the sprint goal?
-
Team Expertise Consideration
-
Does prioritization consider the team's current capabilities?
- Were tasks assigned that match the team’s expertise and capacity for delivery?
- Was knowledge required for each task matched with the available skills in the team?
-
Are any high-priority items risky due to knowledge gaps?
- If items are highly prioritized but the team lacks expertise, was this risk acknowledged and mitigated (e.g., through research spikes)?
-
Does prioritization consider the team's current capabilities?
-
Balancing Effort and Value
-
Were backlog items evaluated based on both effort and value?
- Did the team consider the estimated effort required to complete each item compared to the value it would deliver?
- Were high-value, low-effort items prioritized appropriately?
-
Were backlog items evaluated based on both effort and value?
- Flexibility in Prioritization
-
Is there flexibility in the prioritization to adapt during the sprint?
- Were contingency items discussed in case the team delivers more than expected?
- Were lower-priority items queued in a way that allows them to be picked up if time permits?
-
Alignment with Sprint Goal
-
Collaboration Between Product Owner and Development Team
-
Did the product owner and development team collaborate to finalize prioritization?
- Was the prioritization a shared decision, reflecting both value and technical considerations?
- Were any disagreements about prioritization resolved through negotiation, considering both business value and development complexity?
-
Were trade-offs between competing priorities discussed?
- Was there a conversation about which items to deprioritize, delay, or split due to constraints such as time, effort, or expertise?
- Were those trade-offs made transparently, with team and stakeholder input?
-
Did the product owner and development team collaborate to finalize prioritization?
-
Feedback Loops:
Objective: Embed mechanisms to gather feedback and refine work throughout the sprint, ensuring adaptability and continuous improvement.
-
Mechanisms for Early Feedback
-
Are feedback loops built into the sprint plan?
- Were checkpoints or opportunities for feedback from stakeholders or users discussed during sprint planning?
- Is feedback expected from completed tasks before the sprint ends (e.g., early demos, prototypes)?
-
Is the team prepared for feedback at key stages?
- Are specific tasks or deliverables chosen for early review and feedback?
- Were these stages scheduled or highlighted in the sprint plan?
-
Are feedback loops built into the sprint plan?
-
Stakeholder and User Feedback During the Sprint
-
Are backlog items flexible enough to adjust based on feedback?
- Did the team discuss the potential need to refine or rework items mid-sprint based on feedback?
- Is the sprint plan designed to handle change without disrupting the sprint goal?
-
Was feedback from previous sprints considered in planning?
- Were lessons learned from past retrospectives or reviews incorporated into the current sprint plan?
-
Are stakeholders involved in providing feedback?
- Were specific points for involving stakeholders discussed, especially on high-priority or complex items?
- Is there a clear process for gathering and integrating external feedback?
-
Are backlog items flexible enough to adjust based on feedback?
-
Internal Team Feedback
-
Is there a structure for internal feedback during the sprint?
- Did the team agree on having internal reviews or check-ins to assess progress and challenges?
- Are daily standups used effectively to surface feedback from team members on blockers, progress, or potential improvements?
-
Does the team plan to adapt tasks based on internal feedback?
- Were any changes to tasks or priorities discussed, contingent on internal feedback loops?
-
Is there a structure for internal feedback during the sprint?
This section ensures that feedback loops are embedded throughout the sprint, both from internal team members and external stakeholders, allowing for continuous adaptation and improvement.
-
Mechanisms for Early Feedback
-
Clarification of Unknowns:
Objective: Identify knowledge gaps during sprint planning and create a strategy for discovery during the sprint.
-
Identifying Knowledge Gaps
-
Were potential uncertainties or unknowns discussed?
- Did the team and product owner identify areas of the backlog where knowledge gaps exist (e.g., technical uncertainty, incomplete requirements)?
-
Were any assumptions flagged for validation?
- Were assumptions explicitly stated and plans made to validate or challenge them during the sprint?
-
Are knowledge dependencies clearly identified?
- Did the team recognize dependencies on external knowledge, teams, or stakeholders?
-
Were potential uncertainties or unknowns discussed?
-
Planning for Knowledge Discovery
-
Is there a knowledge discovery plan in place?
- Were time and resources allocated for research, experimentation, or spikes to address unknowns during the sprint?
-
Were learning tasks (spikes, prototyping, research) included in the sprint?
- Are there specific tasks aimed at reducing uncertainty, such as proofs of concept or research items?
-
Are mechanisms in place for revisiting or adjusting based on new knowledge?
- Does the sprint plan allow for flexibility if new discoveries change the approach or scope?
-
Is there a knowledge discovery plan in place?
-
Collaboration to Resolve Uncertainties
-
Are stakeholders and subject matter experts involved to resolve knowledge gaps?
- Were external parties, like stakeholders or experts, identified and included in the plan to provide information when needed?
-
Are stakeholders and subject matter experts involved to resolve knowledge gaps?
This checklist ensures that knowledge gaps are proactively addressed during sprint planning and that a strategy is in place for discovering and filling those gaps as the sprint progresses.
-
Identifying Knowledge Gaps
-
Realistic Commitment:
Objective: Commit to a sprint scope that is achievable based on the team’s capacity, knowledge, and discovery efficiency.
-
Assessing Team Capacity
-
Was the team’s velocity or capacity evaluated based on historical data?
- Did the team discuss their previous velocity or sprint capacity and use it to gauge how much work to commit to?
-
Did the team realistically estimate the effort for each backlog item?
- Were tasks broken down and estimated based on the team’s experience, and was the workload balanced accordingly?
-
Did the team consider the time needed for knowledge discovery and spikes?
- Was time allocated for learning, researching, or reducing uncertainties built into the sprint plan?
-
Was the team’s velocity or capacity evaluated based on historical data?
-
Feasibility of Commitment
-
Were risks and potential blockers accounted for in planning?
- Did the team plan for any known obstacles (technical, resource, or otherwise) that could impact the sprint's progress?
-
Does the team feel confident in their ability to deliver?
- Was there a consensus within the team on whether the commitment is realistic given their skill sets, capacity, and discovery tasks?
-
Were risks and potential blockers accounted for in planning?
-
Adaptability and Buffer Time
-
Is there flexibility built into the sprint for unexpected challenges?
- Did the team leave some buffer in the sprint to accommodate unforeseen issues or necessary pivots?
-
Were discussions held about adjusting scope if new discoveries emerge?
- Did the team agree on how to handle adjustments in the scope based on learning or changing priorities?
-
Is there flexibility built into the sprint for unexpected challenges?
This section ensures the team commits to a realistic and achievable scope that takes into account both known work and discovery-based tasks. It promotes a sustainable workload while accounting for uncertainties.
-
Assessing Team Capacity
-
Contingency Plan:
Objective: Prepare for knowledge gaps or unexpected challenges that could arise during the sprint, ensuring the team can adapt without disrupting the sprint goal.
-
Identifying Potential Risks
-
Were potential risks and uncertainties discussed?
- Did the team identify and document areas where uncertainties or challenges are most likely to arise (e.g., technical unknowns, dependencies)?
-
Were contingency scenarios considered?
- Did the team discuss what might happen if certain tasks take longer or require more effort than estimated?
-
Were potential risks and uncertainties discussed?
-
Building Flexibility into the Sprint
-
Is there buffer time allocated in case of issues?
- Was buffer time added to handle unexpected complications or new discoveries?
-
Is there a plan for handling incomplete tasks?
- Did the team establish a process for handling tasks that may not be completed during the sprint?
-
Is there buffer time allocated in case of issues?
-
Mitigation of Risks from Unknowns
-
Are contingency plans discussed in case of unforeseen discoveries?
- Did the team consider potential pivots or alternative paths if knowledge gaps cannot be filled in the expected timeframe?
-
Are contingency plans discussed in case of unforeseen discoveries?
-
Planning for External Dependencies
-
Were external dependencies considered?
- Did the team account for dependencies on other teams, vendors, or stakeholders that could delay progress?
-
Is there a fallback plan for delays in dependencies?
- Was a fallback plan created in case external resources or dependencies aren't available as expected?
-
Were external dependencies considered?
-
Adjusting Scope or Priorities
-
Is there a process for adjusting scope based on feedback or challenges?
- Did the team discuss how to reduce scope or shift priorities mid-sprint if necessary without losing sight of the sprint goal?
-
Were lower-priority backlog items identified for potential removal?
- Is there a clear understanding of which items can be deprioritized if the team needs to focus on critical challenges?
-
Is there a process for adjusting scope based on feedback or challenges?
This checklist ensures that the team has built flexibility into their sprint, so they can quickly adapt to changes or challenges without derailing the sprint's success.
-
Identifying Potential Risks
This checklist ensures that prioritization decisions are made thoughtfully, balancing business value, team capabilities, and the sprint goal. This structured approach keeps the team aligned with the most valuable work while managing risks and complexity.
This checklist ensures Sprint Planning is both knowledge-driven and aligned with flow principles.
Sprint Goal Checklist
To align the sprint goal with the Psychological State of Flow, the goal must include:
-
What to do:
-
Is the goal specific and clear?
Check if the team understands exactly what must be delivered by the end of the sprint. Are specific backlog items tied to a clear and concise objective? Does everyone articulate the same understanding when asked?
-
Is the goal tangible?
Evaluate whether the sprint outcome is measurable or observable (e.g., working features, resolved defects). Can the team envision what "done" looks like?
-
Does it focus on a single, achievable objective?
Assess if the goal is narrowly focused enough that the team can achieve it without overloading their capacity or splitting focus.
-
Is the goal specific and clear?
-
How to do it:
-
Are there clear steps or approaches suggested?
Examine whether the team has an understanding of how they will approach each backlog item, using known processes, tools, or frameworks. Is there shared alignment on the approach?
-
Is the approach realistic given team capabilities?
Verify if the outlined steps match the team’s skills, resources, and experience. Do team members feel confident they know how to proceed with the tasks?
-
Is technical feasibility discussed?
Evaluate whether the team has considered technical challenges, dependencies, or uncertainties and addressed them during the planning session.
-
Are there clear steps or approaches suggested?
-
Next steps to take:
- Does the goal provide a clear sense of the next iteration’s direction? Confirm whether the sprint goal ties into a larger product or project roadmap, with defined next steps to ensure continuity and sustained flow after the sprint ends.
-
Is there clarity on how future challenges will be approached?
Assess if the team anticipates potential follow-up work or new insights from the current sprint. Are next steps dependent on discoveries or user feedback?
-
Flow-Specific Auditing Questions:
-
Does the goal balance challenge and skill?
Ensure the goal provides enough challenge to engage the team, but not so much that it overwhelms them, a core element of maintaining flow.
-
Is the sprint goal motivating and clear enough to promote focus?
Determine if the goal inspires commitment and focus, essential for the team to enter a flow state. Does the team feel excited and ready to concentrate fully on the goal?
-
Does the goal balance challenge and skill?
Once these elements are checked and confirmed, the team is likely in a position to not only work effectively but also stay in a productive, flow-like state during the sprint.
Daily Scrum Checklist
The Daily Scrum is a 15-minute event for the Developers of the Scrum Team.
Here’s a Daily Scrum Checklist from a knowledge-centric perspective, focusing on alignment, knowledge flow, and team productivity:
-
Alignment with Sprint Goal
-
Was the sprint goal revisited?
- Did the team remind themselves of the sprint goal during the Daily Scrum?
- Are updates framed in relation to how they contribute to the sprint goal?
-
Were any blockers discussed that could impact the sprint goal?
- Did team members raise issues that may hinder progress?
- Were these blockers escalated to the right person for resolution?
-
Was the sprint goal revisited?
-
Tracking Progress
-
Is the team aware of progress toward the sprint goal?
- Was progress toward the sprint goal clearly communicated, and is the team on track?
- Did the team express confidence or concern about achieving the goal?
-
Is the team aware of progress toward the sprint goal?
-
Knowledge Flow
-
Did everyone share relevant updates?
- Did each team member provide meaningful updates, including what they learned or discovered since the last Scrum?
- Were knowledge gaps surfaced during the meeting?
-
Were dependencies or handoffs discussed?
- Were there any new dependencies between team members, and were they clarified?
- Were key handoffs or coordination points for the day highlighted?
-
Did everyone share relevant updates?
-
Plan Adjustments
-
Was the plan adjusted based on new insights or challenges?
- Did any new knowledge or insights necessitate changes to the plan?
- Were any priorities shifted or tasks re-assigned to adapt to newly surfaced information?
- Did the plan change due to the changed priorities or requirements from the PO?
- Did the plan change due to external dependencies?
-
Were learning tasks or spikes mentioned in the Scrum?
- Did the team discuss ongoing research, experiments, or discovery activities?
- Did the team discuss are these tasks proceeding according to plan?
- Are these tasks explicitly visualized on the board?
-
Was the plan adjusted based on new insights or challenges?
-
Assigning Tasks Based on Capabilities
-
Were tasks and user stories matched to appropriate team members?
- Were assignments made considering who is best suited for each task?
- Did team members have input into which tasks they would undertake?
-
Were tasks and user stories matched to appropriate team members?
-
Promoting Optimal Challenge Levels (Flow and Motivation)
-
Did team members report engagement with their tasks?
- Was there any mention of being anxious or bored with tasks that are either too easy or too challenging?
- Did the Scrum reveal whether any team member was either disengaged or feeling overwhelmed?
-
Does each task provide the right level of challenge for the assigned team member?
- Are tasks neither too easy (leading to boredom) nor too difficult (causing anxiety)?
- Were team members enthusiastic about their assignments?
-
Was the balance between task difficulty and skill level discussed?
- Did the team evaluate potential obstacles and complexities of tasks?
- Were less experienced members given opportunities to learn with appropriate support?
-
Were strategies discussed to maintain team members in a flow state?
- Are tasks structured to allow for deep focus without unnecessary interruptions?
- Is the workload designed to keep team members engaged throughout the sprint?
-
Are mechanisms in place to adjust tasks if the challenge-skill balance shifts?
- Can tasks be reallocated if they prove too easy or too difficult?
- Is there flexibility to modify tasks based on ongoing feedback?
-
Were opportunities to support or collaborate identified?
- Did team members offer to assist others facing challenges?
- Were collaborative efforts discussed for tackling more complex issues?
-
Did team members report engagement with their tasks?
-
Encouraging Skill Development
-
Were knowledge gaps identified and addressed?
- Did the team discuss any skills needed that are currently lacking?
- Are training or research tasks included in the sprint to fill these gaps?
-
Were knowledge gaps identified and addressed?
-
Ensuring Team Collaboration
-
Was collaboration encouraged to leverage collective skills?
- Are complex tasks planned to be tackled collaboratively?
- Is there a culture of supporting each other to overcome challenges?
-
Was collaboration encouraged to leverage collective skills?
-
Unplanned Knowledge Work
-
Was any unplanned work discussed?
- Did the team encounter tasks or challenges they initially thought they understood but realized they didn’t?
-
How is unplanned work being managed?
- Did the team adjust the sprint plan to accommodate this new work, or are they seeking additional help?
-
Is unplanned knowledge work impacting the sprint goal?
- Were conversations held about how this unplanned work might affect progress toward the sprint goal?
-
Was any unplanned work discussed?
-
Multitasking
-
Is multitasking affecting progress?
- Are team members working on multiple tasks simultaneously, and is this affecting their focus or productivity?
-
Is multitasking accepted, discouraged, or mandated?
- Is multitasking happening due to external pressures or team dynamics, and does it hinder task completion?
-
Is multitasking affecting progress?
This checklist ensures that the Daily Scrum promotes effective communication, alignment, and continuous adaptation, reinforcing flow and learning.
Conclusion
Incorporating a knowledge-centric perspective into Scrum not only enriches the framework but also enhances its effectiveness in addressing the cognitive challenges inherent in software development. Scrum’s cyclical processes of socialization, externalization, combination, and internalization of knowledge create a dynamic environment where information flows freely and efficiently. Daily Scrum meetings and collaborative work sessions become powerful venues for converting individual insights into collective understanding, thereby accelerating the Knowledge Spiral throughout the organization.
Utilizing a Burndown chart to track unanswered questions offers a fresh way to visualize and manage knowledge work. This approach emphasizes the importance of closing knowledge gaps, providing teams with a clear, motivating, and transparent method to gauge their progress in real-time.
It's evident that Scrum, more than just a framework for managing complex software projects, is a powerful tool for fostering a state of Flow and facilitating knowledge-centric development. Through its structured yet adaptable practices, Scrum aligns perfectly with the principles of Flow as articulated by Mihaly Csikszentmihaly.
The iterative nature of Scrum, with its clear and attainable goals set through the Sprint Goal and the Product Backlog, ensures that team members are consistently engaged with tasks that are challenging yet achievable. This alignment of tasks with individual capabilities and the provision of immediate feedback through regular Scrum ceremonies like Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Reviews, and Retrospectives, creates an ideal environment for team members to achieve and maintain Flow. In this state, they are not only more productive and efficient but also find greater satisfaction and fulfillment in their work.
Moreover, the knowledge-centric perspective of Scrum – understanding and bridging the knowledge gaps between what a developer knows and what they need to know – plays a pivotal role in sustaining this state of Flow. By ensuring that tasks are neither too simplistic to cause boredom nor too complex to induce anxiety, Scrum maintains a delicate balance that is conducive to continuous learning and growth. This approach not only leads to the development of high-quality software but also contributes to the personal and professional development of team members.
Scrum, when viewed through the lenses of the KnowledgE-centric perspective, transcends its role as a project management methodology. It emerges as a comprehensive approach that not only ensures the efficient delivery of software projects but also nurtures an environment of continuous improvement, knowledge enhancement, and deep work engagement. This holistic perspective on Scrum provides invaluable insights for teams and organizations striving to optimize their software development processes while also fostering a fulfilling and productive work environment for their members.
Embracing this knowledge-centric approach ultimately leads to more informed decision-making, greater innovation, and successful project outcomes. As teams continue to navigate the complexities of software development, this perspective ensures that they remain agile, responsive, and equipped to meet the evolving demands of their projects.
Works Cited
1. Schwaber, K. and Sutherland, J. (2020) The Scrum Guide. https://scrumguides.org/scrum-guide.html
2. Csikszentmihalyi, M. 1990. Flow: the psychology of optimal experience. United States of America: Harper & Row.
3. Schaffer, O. 2013. Crafting Fun User Experiences: A Method to Facilitate Flow. Human Factors International Whitepaper. Retrieved from: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=9760324565241258858
4. Sutherland, J. (2014) Scrum: The Art of Doing Twice the Work in Half the Time. Crown Business, New York.
5. Ken Schwaber and Mike Beedle. 2001. Agile Software Development with Scrum (1st. ed.). Prentice Hall PTR, USA.
6. Nonaka, I. and Takeuchi, H. (1995). The knowledge-creating company: how Japanese companies create the dynamics of innovation. Oxford University Press
How to cite:
Bakardzhiev D.V. (2023) Scrum: A Knowledge-centric Perspective https://docs.kedehub.io/kede-manage/kede-manage/kede-scrum.html
Getting started


